Advantages and Disadvantages of Handheld GPS
Actually there are many types of GPS, not just handheld / portable GPS, but also GPS Navigation and GPS Smartphone. For the first of these I will discuss in advance about the GPS handheld, and now I will explain the advantages and disadvantages of GPS handheld. |
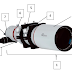
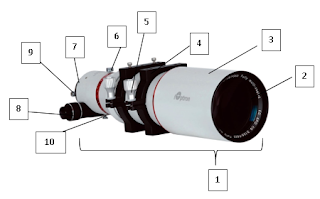
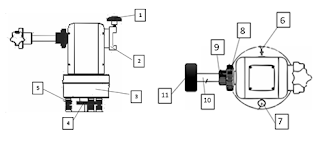
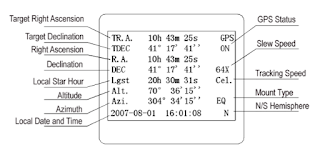
| Handheld GPS |
The use of barometric altimeter sensors usually must first be done altitude calibration somewhere. We can also use this barometric altimeter to plot air or ambient pressure from time to time, which can help to observe changes in weather conditions.
The advantage of this GPS compass is that it is not influenced by the magnetic field and can guide the direction accurately as it is guided by signals from the satellites (not the buit-in compass sensor). This tool is certainly very helpful when measuring the direction of Qibla.
The area is remote with no phone signal and does not have internet. We recommend choosing a handheld GPS device. Maps are already stored inside, though the images are very standard, such as the appearance of road maps and soil contours, the data maps in the handheld GPS more complete, but usually sold separately (for each country) and the price is quite expensive. Maps do not need to be installed or downloaded. Because portable GPS has been installed one country map when marketed.
GPS handheld is better, more durable, waterproof and suitable for outdoor activities. Users need not be afraid of the natural conditions, because handheld GPS devices or portable GPS are designed for nature activities. Using this GPS we can find the way when through high-sensitivity wilderness, which acquires satellite signals quickly and tracks locations in challenging conditions such as trees and cliffs.
The battery can be replaced because it uses AAA batteries. One portable GPS device can last up to 25 hours. Very suitable for adventure activities in areas far from electrical energy.
But the obstacle, GPS handheld in terms of price is still quite expensive, for a GPS device ranges between Rp. 2,000,000.00 to Rp.10.000.000,00 or about $ 150 USD to $ 750 USD.
The disadvantages of all GPS, including GPS handhelds are GPS will greatly affect the geographical conditions of where we are. GPS will work well if where we are still has a wide sky. The following will be described wherever the GPS will experience a weakness in its use:
1.When someone is in the forest. With the conditions of the trees are so much then the signals that can be received will be a little maybe even no depending on the width of the forest.
2.When someone is in the water or when someone is diving. Do not expect to use this tool when diving.
3. Electronic devices that can emit electromagnetic waves may affect performance degradation rather than GPS.
4. Buildings. Not only when inside the building, being between 2 tall buildings will also cause an effect like being in a valley.
5. Signals that bounce, eg when in between high-rise buildings, can disrupt the calculation of navigation tools so that navigation tools can indicate the wrong position or not accurate.
6. Glass film car, especially metal-containing.