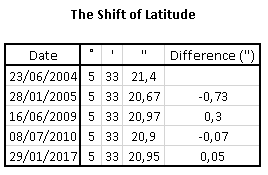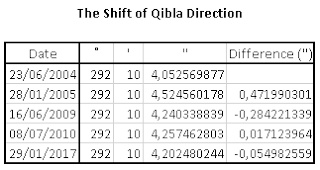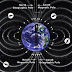
The Poles
Pole are defined as an axis, the polar division of the earth exists a variety, including the magnetic poles of the earth and the geographical poles of the earth:
1. Earth's Magnetic Pole
Have you ever had a compass? the compass you have will show you the direction of North, East, South and West. This direction is a magnetic direction. The direction indicated by the compass is the result of the pulling force of the Earth's magnetic poles.
The Earth's magnetic pole is not right at the Earth's axis, the Earth's magnetic pole position is fluid, the North direction is indicated as a magnetic North that is affected by the gravitational pull force of the earth, so it has a different value every day, and every where.
2. Earth's Geography Pole
This pole is the original axis of the earth, its position remains at one point, and does not change. The polar position is at 90 degrees from the Equator (North Pole), and also -90 degrees from the Equator (South Pole). The rotation motion of the earth for approximately 24 hours rotates through this axis.
Compass is a tool that use the magnetic poles of the earth. Although the compass does not show the right direction, it can still be used accurately (leading to Earth's geographical poles) with some corrections, such as declination and inclination.
Magnetic declination is a horizontal shift toward the east or the west. Magnetic Inclination is a vertical shift toward the north or east direction of the compass. The value of this declination changes every day, we can check at Magnetic Declination. Meanwhile, the inclination value varies everywhere, depending on the position of the compass in the latitude. If the compass is in the southern latitudes, then the inclination of the compass will lean towards the south, and vice versa.
Points of The Compass
Point of Compass is a guide to determine direction, usually used in Navigation system. There are 8 principle directions in this point of the compass system. Namely : North, Northeast, East, Southeast, South, Southwest, West, Northwest.
There are several ways to know the true winds, one of them is by using a compass as I mentioned above. Another way is to use the Sun :
1. Shortest shadow
Plug the stick to the ground in a flat position. With this method we are only looking for the shortest shadow when meridian pass/zawal (Sun at the zenith point), then we see the Sun declination value, if the declination of the Northern Sun is positive, so the shadow of the Sun points south direction, if the declination is South or the value is negative, so the shadow of the Sun leads North direction. But this method has a weakness, if the Sun is right above where we are, so there will be no shadow.
2. Shadows before and after Merpass / zawal
Plug the stick to the ground in a flat position, then make 1 to 3 circles around the stick with the stick as the center point. Observe before merpass, and observe the shadow that the end of the line touching the circle lines you have created. And make a point on the tangent. Observe after merpass, and observe the shadow that the end of the line touching the circle lines you have created. And make a point on the allusion. Connect the 2 points. The first point shows the true West direction, the second point shows of the true East direction.
3. Use the azimutal value of the Sun
This method is practically easier, but this method uses calculations. the first way is Shooting the Sun, then Counting the azimut of the Sun and then pointing towards 0 value (True North).
The above ways will be explained in another article.
Pole are defined as an axis, the polar division of the earth exists a variety, including the magnetic poles of the earth and the geographical poles of the earth:
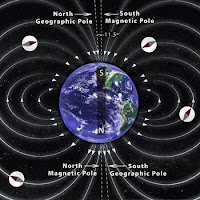 |
| The Poles of the Earth Source : http://www.calendarinthesky.org |
Have you ever had a compass? the compass you have will show you the direction of North, East, South and West. This direction is a magnetic direction. The direction indicated by the compass is the result of the pulling force of the Earth's magnetic poles.
The Earth's magnetic pole is not right at the Earth's axis, the Earth's magnetic pole position is fluid, the North direction is indicated as a magnetic North that is affected by the gravitational pull force of the earth, so it has a different value every day, and every where.
2. Earth's Geography Pole
This pole is the original axis of the earth, its position remains at one point, and does not change. The polar position is at 90 degrees from the Equator (North Pole), and also -90 degrees from the Equator (South Pole). The rotation motion of the earth for approximately 24 hours rotates through this axis.
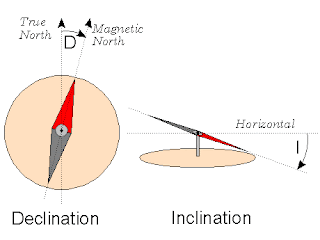 |
| Inclination and Declination of The Compass Source : http://digilander.libero.it |
Magnetic declination is a horizontal shift toward the east or the west. Magnetic Inclination is a vertical shift toward the north or east direction of the compass. The value of this declination changes every day, we can check at Magnetic Declination. Meanwhile, the inclination value varies everywhere, depending on the position of the compass in the latitude. If the compass is in the southern latitudes, then the inclination of the compass will lean towards the south, and vice versa.
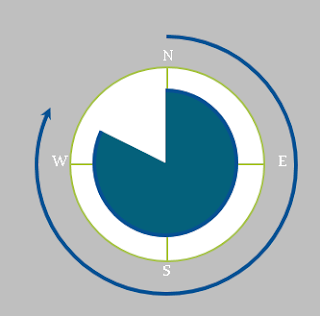
Points of The Compass
 |
| Points of The Compass Source : https://en.wikipedia.org |
There are several ways to know the true winds, one of them is by using a compass as I mentioned above. Another way is to use the Sun :
1. Shortest shadow
Plug the stick to the ground in a flat position. With this method we are only looking for the shortest shadow when meridian pass/zawal (Sun at the zenith point), then we see the Sun declination value, if the declination of the Northern Sun is positive, so the shadow of the Sun points south direction, if the declination is South or the value is negative, so the shadow of the Sun leads North direction. But this method has a weakness, if the Sun is right above where we are, so there will be no shadow.
2. Shadows before and after Merpass / zawal
Plug the stick to the ground in a flat position, then make 1 to 3 circles around the stick with the stick as the center point. Observe before merpass, and observe the shadow that the end of the line touching the circle lines you have created. And make a point on the tangent. Observe after merpass, and observe the shadow that the end of the line touching the circle lines you have created. And make a point on the allusion. Connect the 2 points. The first point shows the true West direction, the second point shows of the true East direction.
3. Use the azimutal value of the Sun
This method is practically easier, but this method uses calculations. the first way is Shooting the Sun, then Counting the azimut of the Sun and then pointing towards 0 value (True North).
The above ways will be explained in another article.